2. Bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers and the global economic and financial crisis
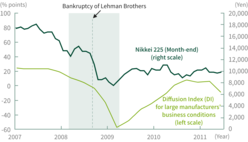
The bankruptcy of U.S. investment bank Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008 accelerated the global financial crisis caused by the U.S. subprime mortgage crisis. The financial turmoil caused serious dysfunction in financial and capital markets. It gave a crushing blow to the world economy, which fell into a global recession. In this situation, major U.S. and European financial institutions suffered from enormous losses related to subprime mortgage loans and related securitized products. In contrast, direct losses incurred by Japanese institutions investing in such securitized products was limited.
Nevertheless, the severe recession also affected the Japanese economy and the stock market. The financial sector faced unfavorable business results, specifically in a worsened profit/loss balance on stocks and increased credit-related costs. Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group (SMFG) posted a consolidated net loss of 373.5 billion yen for fiscal year 2008, due principally to huge expenses for writing off stocks, increased provisions for loan-loss reserves in consideration of deteriorating economic outlooks, and conservative valuations for deferred tax assets.
-
Chapter 1The Financial Crisis and Realignment of the Financial Sector
-
Chapter 2The Birth of SMBC and SMFG
-
Chapter 3Initiatives Pursued by SMBC Banking Units in the Early Years
-
Chapter 3Initiatives Pursued by SMBC Banking Units in the Early Years
-
- Enhancing our retail consulting and payments & consumer finance businesses
- Enhancing corporate financial solutions
- Banking-Securities collaboration in the wholesale securities business
- Challenges facing our global banking business
- Actions by Treasury Unit in preparation for rising interest rates
- Integration of operating systems and administrative functions
-
-
-
Chapter 4Embarking on Fresh Challenges Under New Leadership
-
Chapter 4Embarking on Fresh Challenges Under New Leadership
-
- Changes of leadership and the announcement of our new management policy
- Developing group business strategies
- Addressing antitrust issues
- Completing repayment of public funds
- LEAD THE VALUE
- Enhancing our retail financial consulting business
- Enhancing our corporate solution business
- Enhancing our investment banking business
- Global banking business turnaround
- Upgrading risk management in preparation for Basel II
- Development of human resources
- CSR activities
-
-
-
Chapter 5SMFG’s Response to Global Economic and Financial Turmoil
-
Chapter 6Preparing for the Next Decade
-
Chapter 1Business Model Reform Under Challenging Business Conditions
-
Chapter 1Business Model Reform Under Challenging Business Conditions
-
- Our journey under new leadership (the second decade)
- Focusing on growth industries and businesses
- Reforming domestic business operations
- Promoting banking-securities collaboration in Wholesale Banking Unit
- Structural reform of our retail business
- Meeting the needs of an aging society
- Abenomics and Treasury Unit's nimble portfolio management
- Operating in a negative-interest-rate environment
-
-
-
Chapter 2Enhancing Group Businesses
-
Chapter 3Expanding Our Global Business
-
Chapter 4Enhancing Corporate Infrastructure Under a New Governance Framework
-
Chapter 4Enhancing Corporate Infrastructure Under a New Governance Framework
-
- New leadership and enhancing corporate governance
- Introducing group-wide business units and CxO system
- Improving capital, asset, and cost efficiency
- Pursuing our cashless payment strategies
- Retail branch reorganization
- Customer-oriented business conduct
- Enhancing internal-control frameworks
- Valuing diversity and revision of our HR framework
-
-
-
Chapter 5The Path for Our Future
-
Chapter 6Opening a New Chapter in SMBC Group’s History
